Active Cell refers to the cell that is currently active at the moment. The ActiveCell Object in VBA is used to refer to the Active Cell of the Current Worksheet of the Active Workbook. The ActiveCell has its methods and properties.
So let us start learning.
How to Activate a Cell using VBA?
We can use the Activate method to activate a Cell. We can refer to a cell with the help of Range or Cells Function.
Range("<column>"&"<row>").Activate
Or
Cells(<row_number>,<column_number).ActivateLet us say we wish to select the Range A1:D10 of the Active Worksheet. Thereafter, we activate cell B5 of the Selected Range. You can use the following Sub Procedure to select the range A1:A10 and then activate the cell from the selected range of cells.
Sub activateCellB5()
'select the Range A1:D10 of Active Worksheet
Range("A1:D10").Select
'activate the cell B5
Cells(5, 2).Activate
'change the interior color of active cell
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(230, 210, 240)
End Sub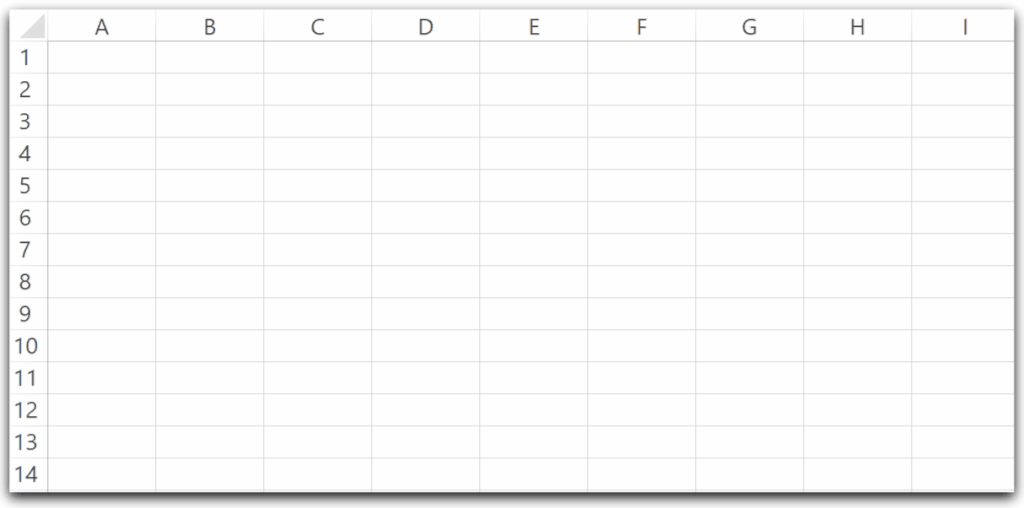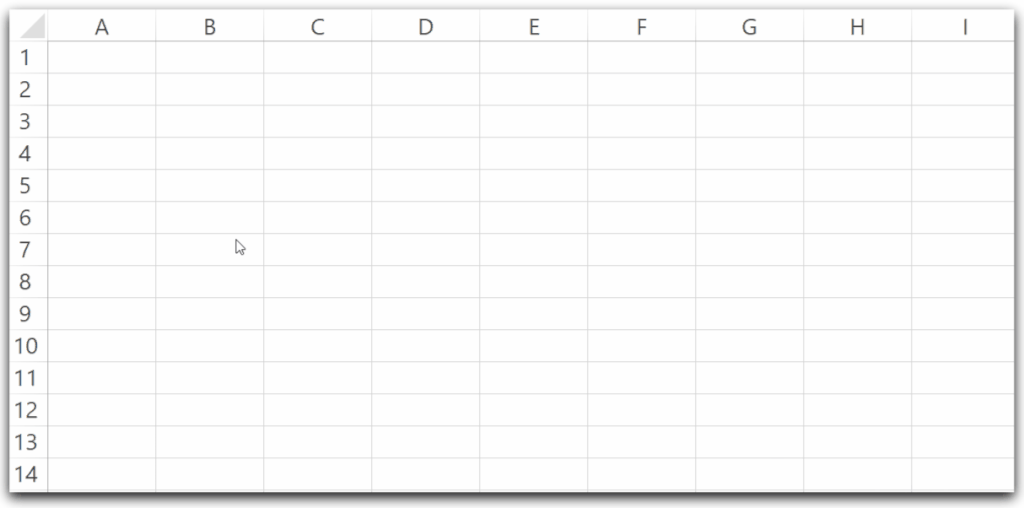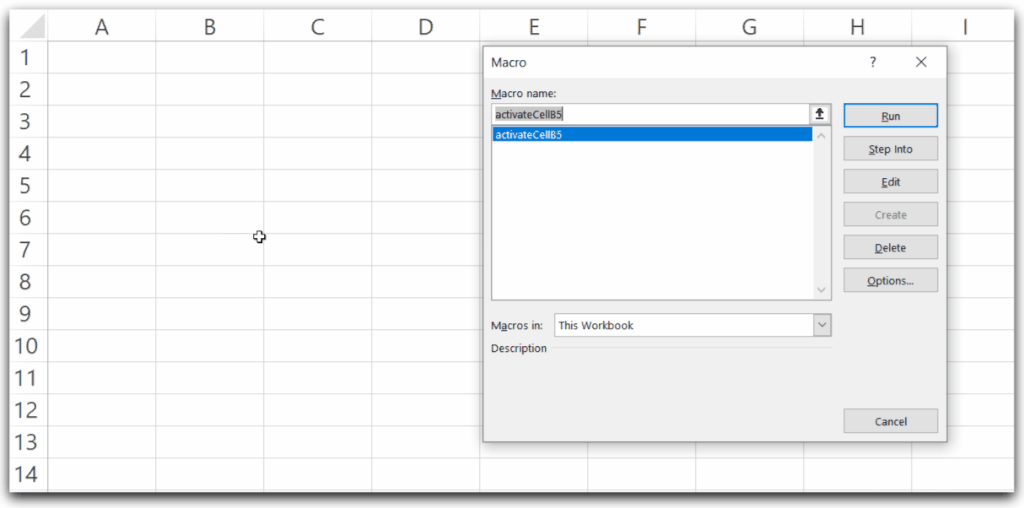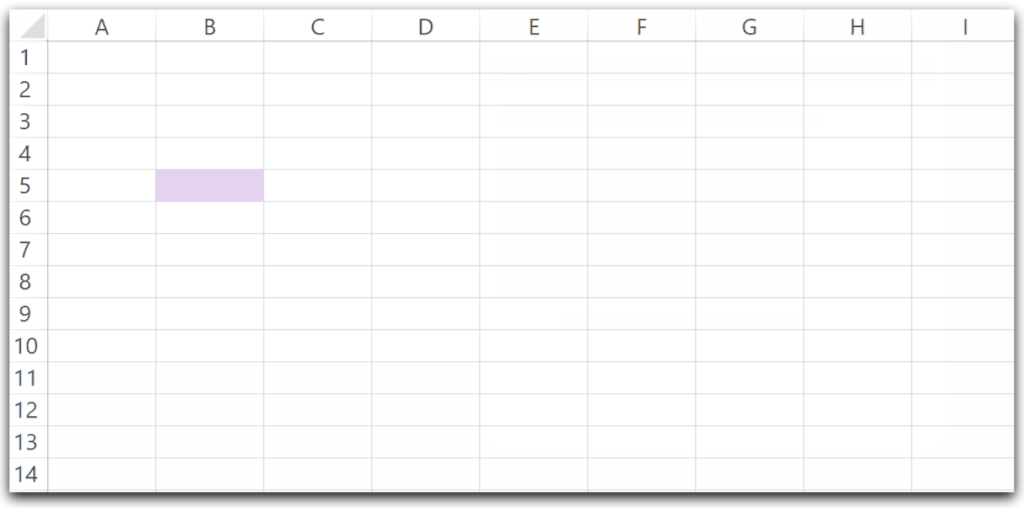
Highlight Range Around Active Cell
We can use the CurrentRegion property of the Active Cell to refer to the range of cells from the top left cell to the bottom right cell around the active cell. Thereafter, we will change the background color of the current region around the active cell.
Also Read: How to Use Active Cell in VBA
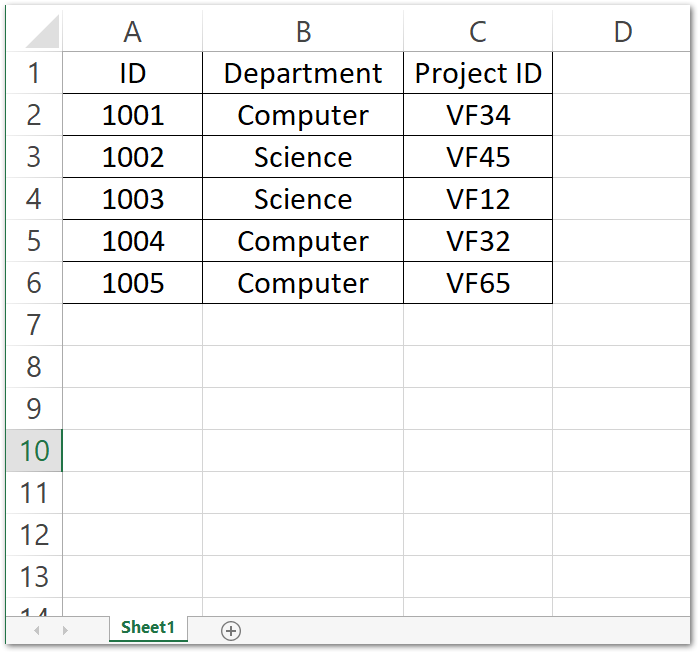
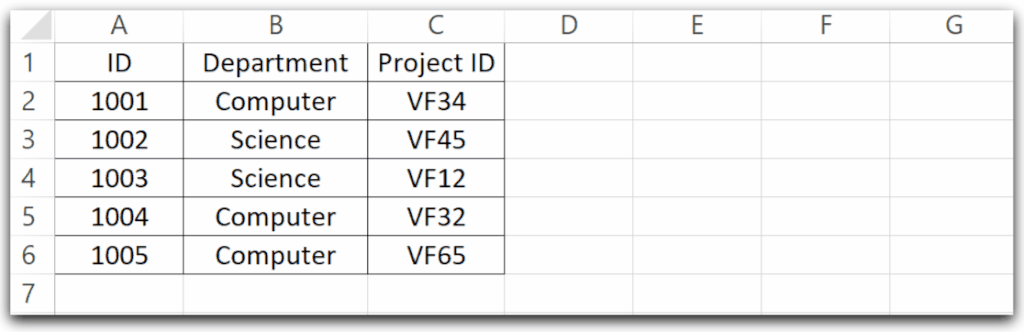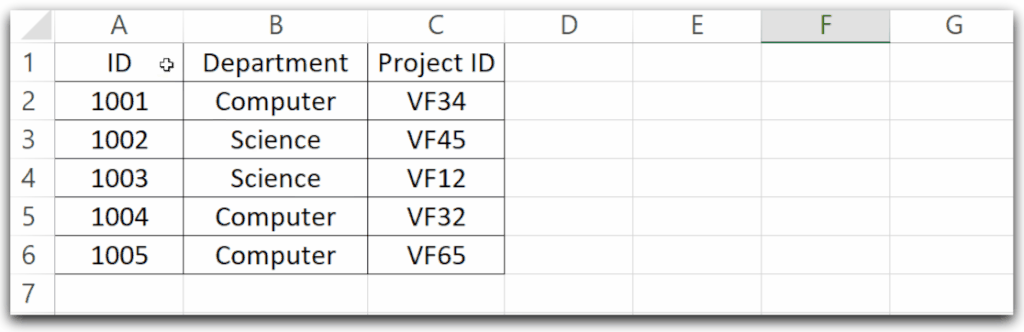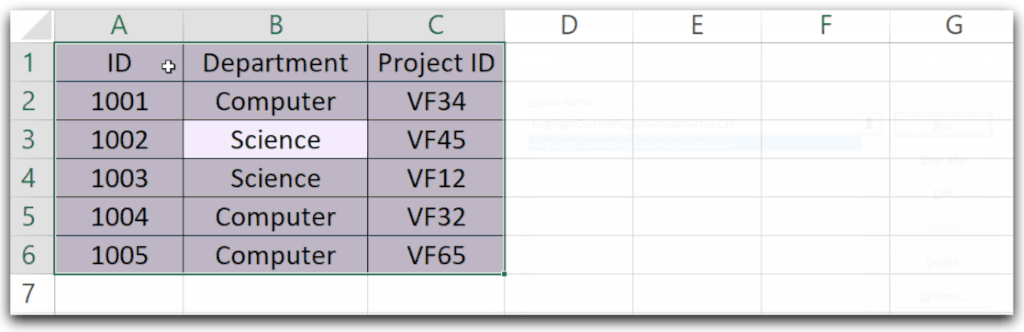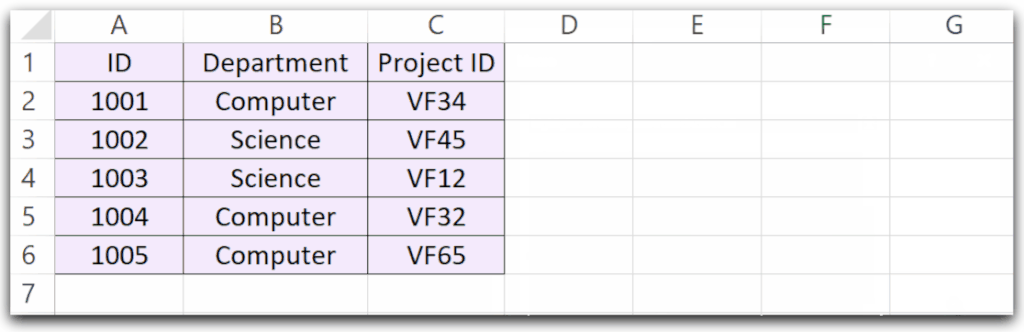
Let us say we have a worksheet named Sheet1 and it has the following data.
You can use the following Sub Procedure. The function is used to generate random lighter shades to highlight.
'a function that returns a random integer between 201 and 255
Function random() As Integer
Do Until random > 200
random = rnd() * 255
Loop
End Function
'sub procedure to highlight area around active cell
Sub highlightCurrentRegionAroundActiveCell()
'highlight current region around active cell
ActiveCell.CurrentRegion.Select
'activate a cell
Range("B3").Activate
'highlight region around active cell
ActiveCell.CurrentRegion.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
End SubActivate the cell to cell A1. When you run this Sub Procedure the following things happen.
- The Range around the Active Cell is selected.
- Cell B3 is activated.
- The random color generated by the RGB function is set as the background color of the Range around the active cell.
Value in Active Cell
We can refer to the Value of the Active Cell with the help of the Value property of the ActiveCell Object. We are using the MsgBox function to print the value in Active Cell.
You can use the following Sub Procedure.
Sub printValueInActiveCell()
'print the value in active cell using VBA
MsgBox ActiveCell.Value
End Sub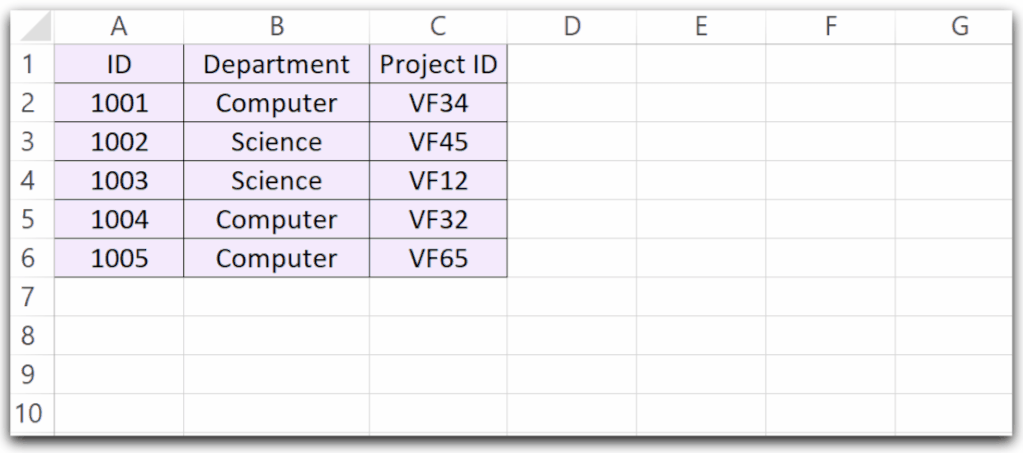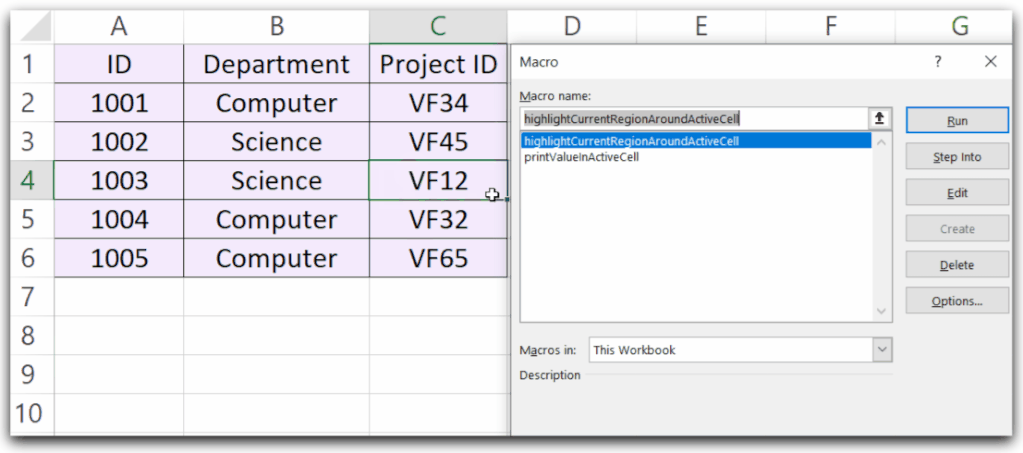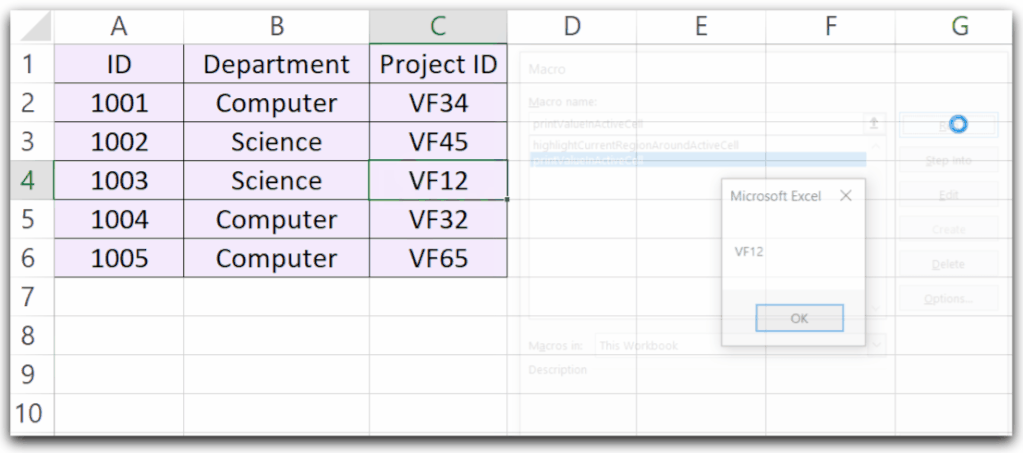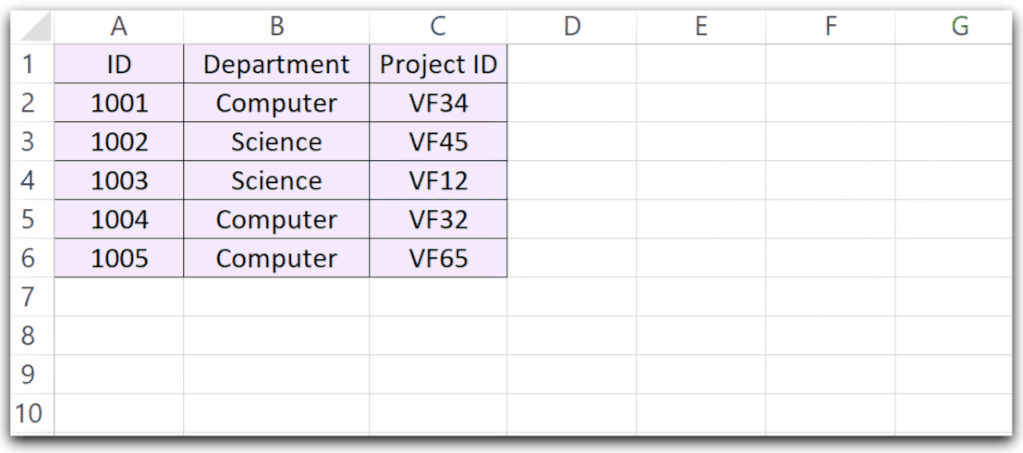
We can clear the contents of Active Cell by using the Clear method.
ActiveCell.ClearSet the Active Cell to an Object
Active Cell refers to the cell which is currently active. We can set a Range Object to refer to the Active Cell.
We can activate a cell and then run this Sub Procedure to change its value using the Range Object.
Sub setActiveCellToRange()
'set the value of active cell to a range variable
Dim myCell As Range
'set the active cell to myCell
Set myCell = ActiveCell
'change the value of myCell value
myCell.Value = "This is new value of Active Cell"
End Sub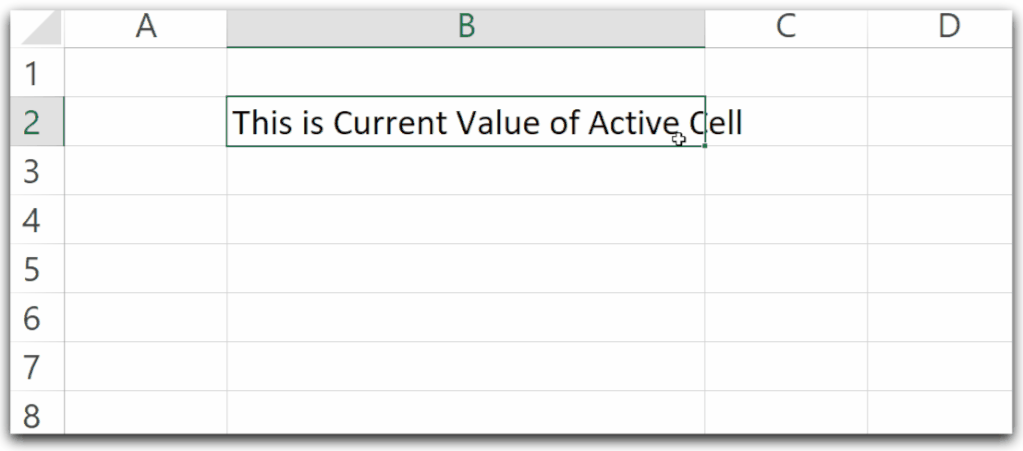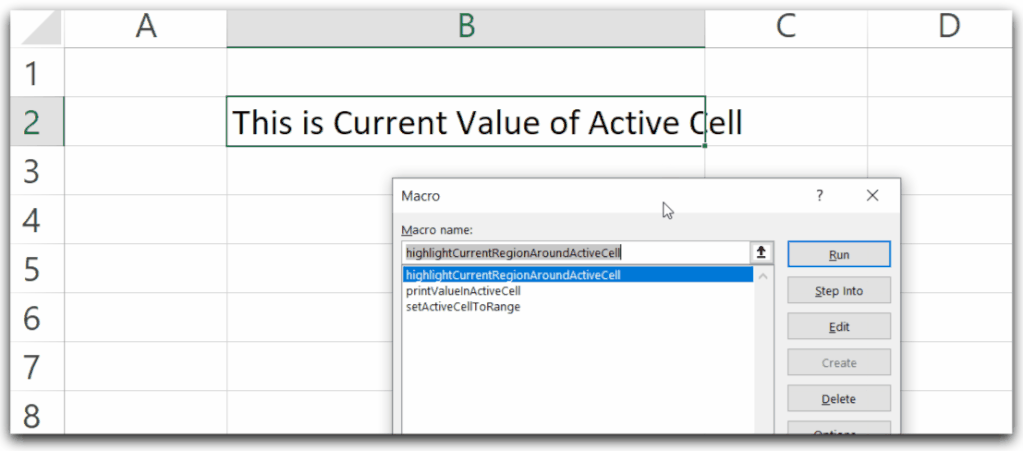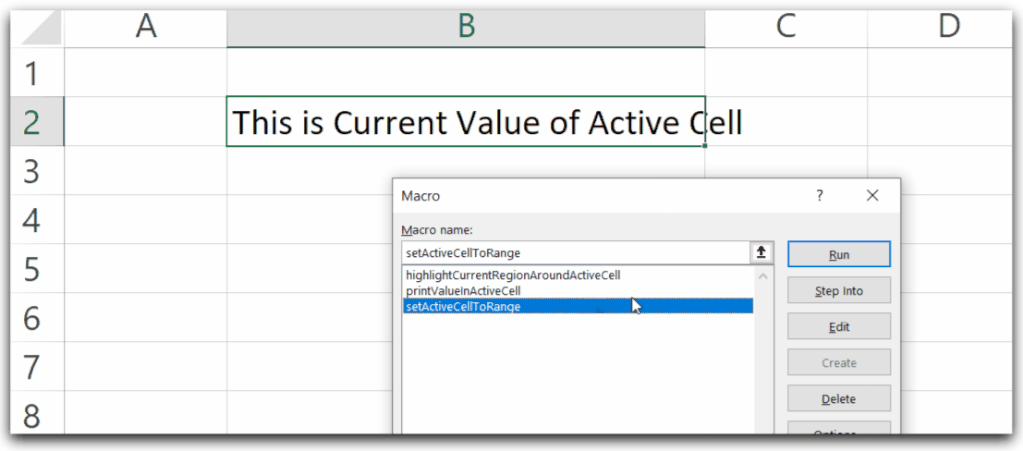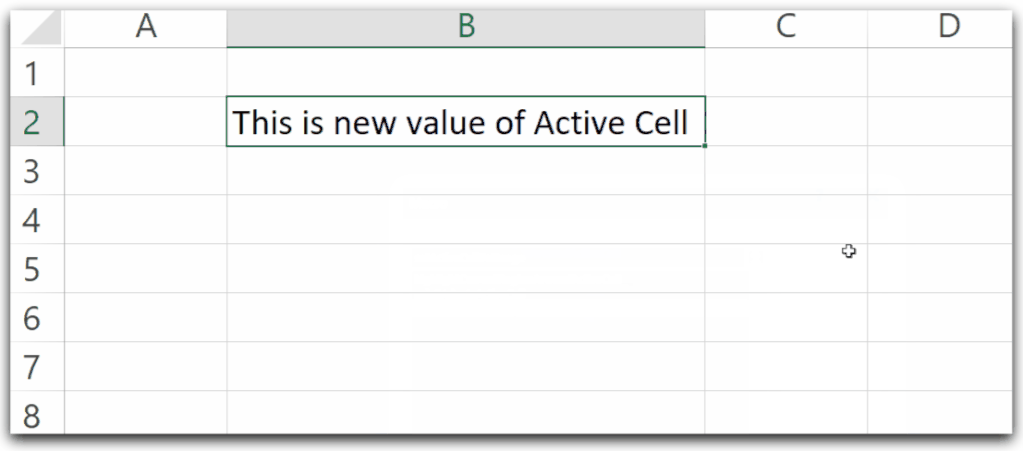
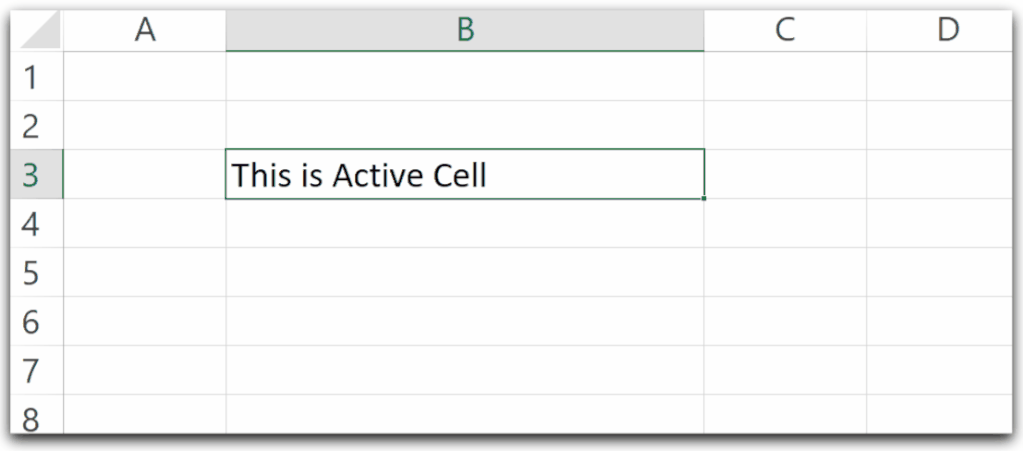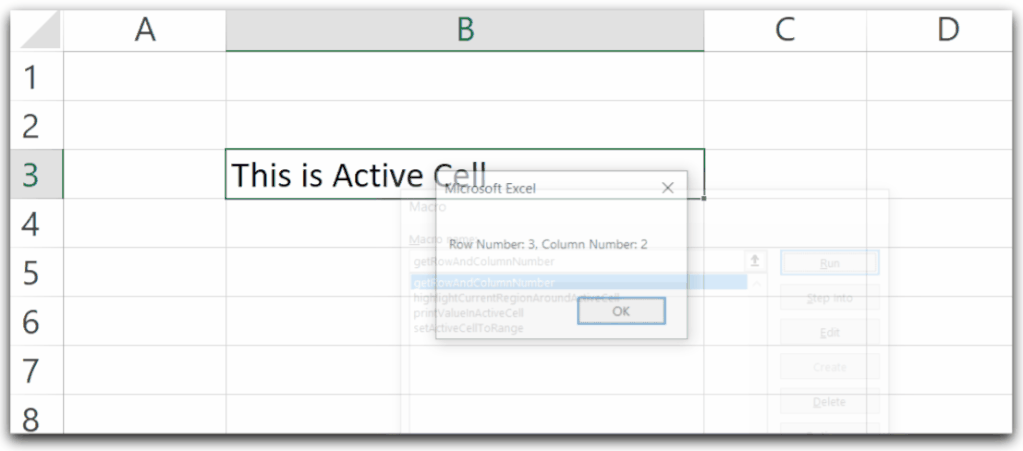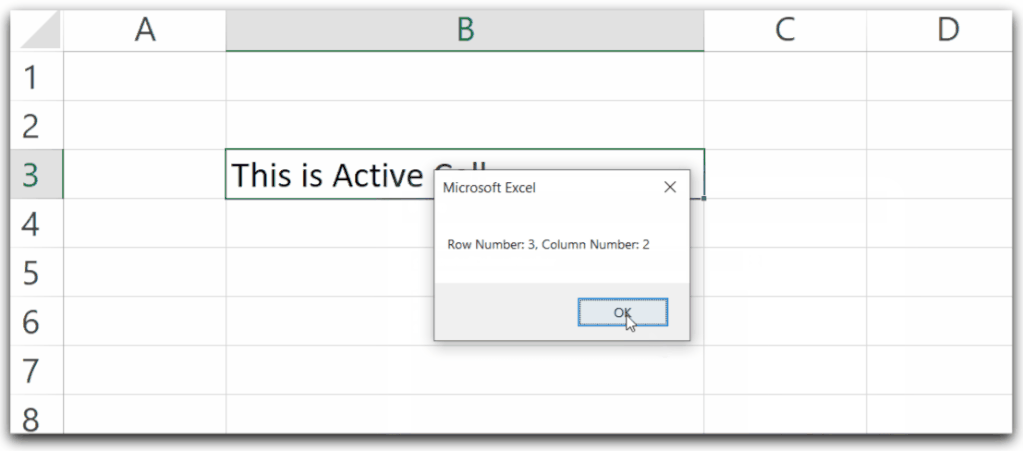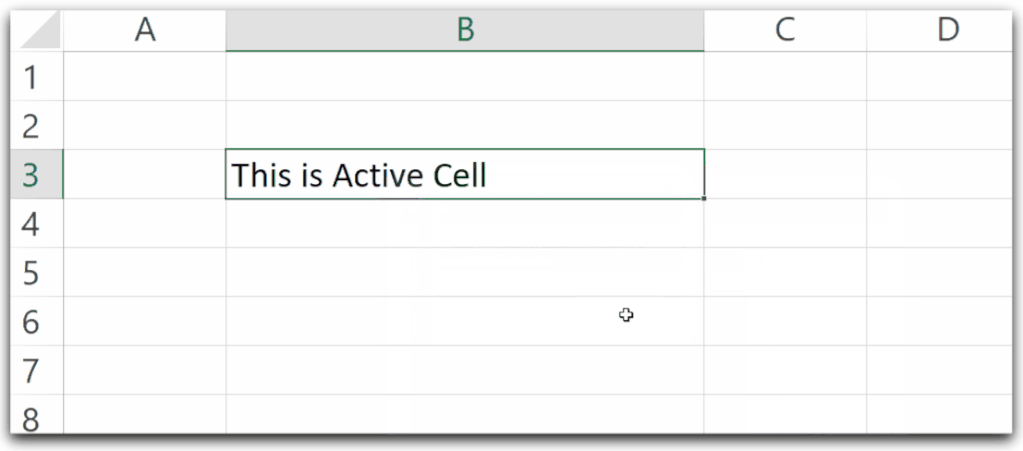
Get the Row Number and Column Number of the Active Cell
We can use the Row and Column property of the ActiveCell object to get the value of the row number and column number respectively.
Sub getRowAndColumnNumber()
'print the value of row number and column number of active cell
MsgBox "Row Number: " & ActiveCell.Row & ", Column Number: " & ActiveCell.Column
End SubWhen you run this Sub Procedure, it will print the value of the row number and column number of the active cell.
Also Read: Cells in VBA – Usage With Examples
Get the Address of Active Cell
We can use the Address property of ActiveCell to print its Address.
ActiveCell.AddressMove the Active Cell using OFFSET
We can use the OFFSET method of Active Cell to move its location row wise and column wise. It has two arguments.
ActiveCell.Offset(<row_offset>,<column_offset>)- row_offset – This is the number of rows that we want to shift from the current address of the active cell. If it is positive then the active cell moves down and if it is negative, the active cell moves up.
- column_offset – This is the number of columns that we want to move from the current location of the active cell. If is positive then the active cell moves to the right and if it is negative then the active cell moves to the left.
For instance, you can use the following Sub procedure to move the active cell from its current location.
Sub moveActiveCell()
'using OFFSET TO MOVE ACTIVE CELL
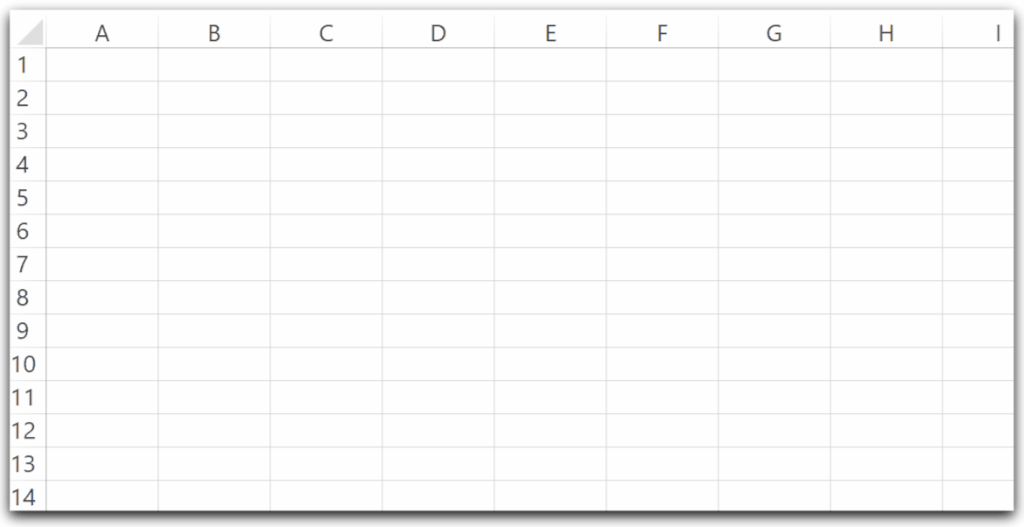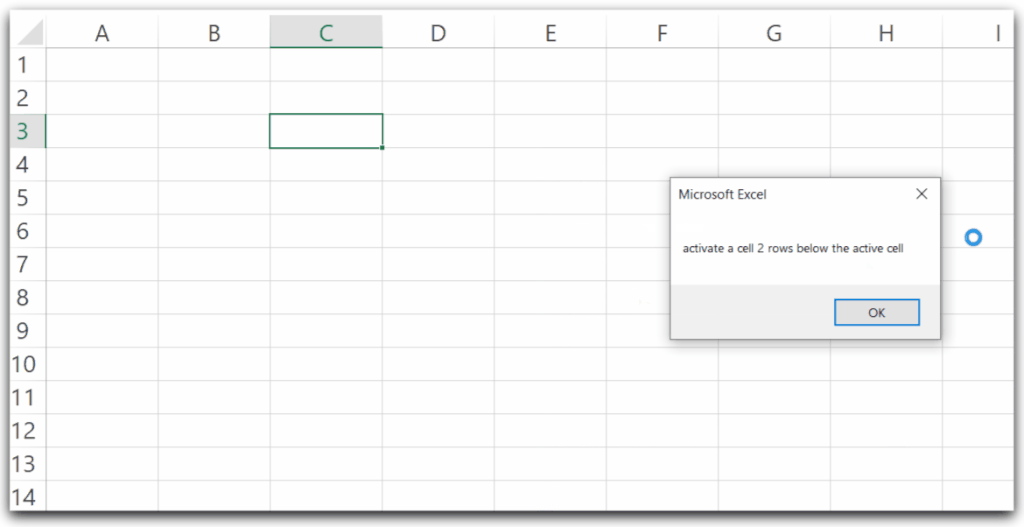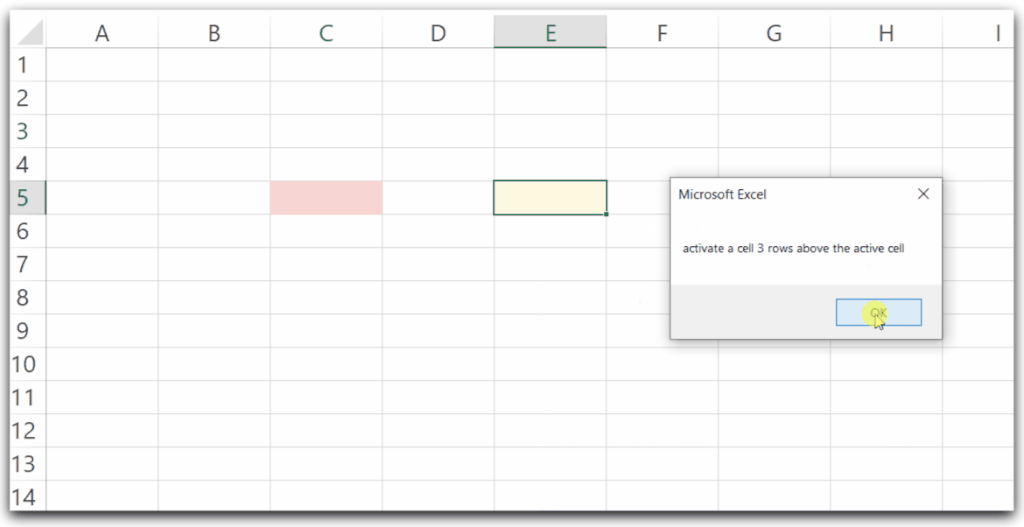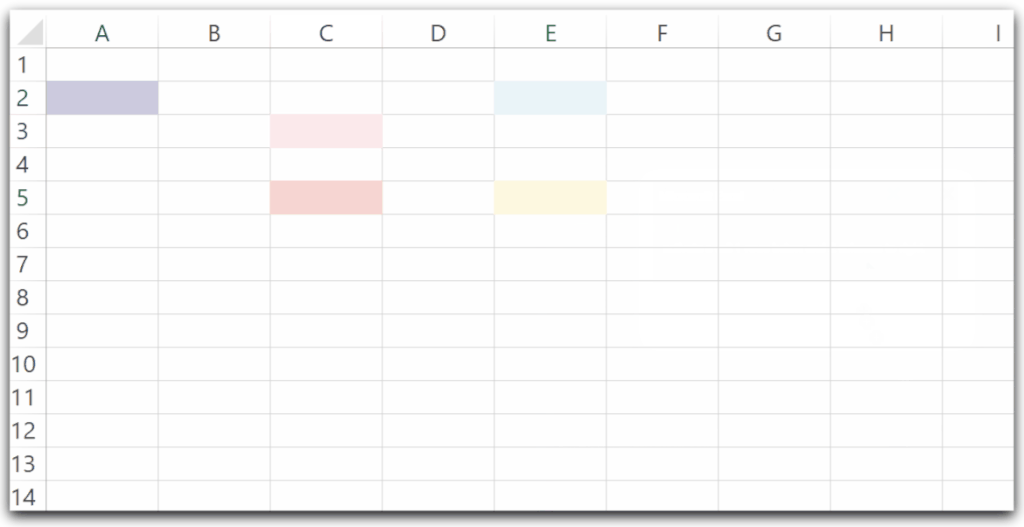
MsgBox ("activate a cell 2 rows below the active cell")
ActiveCell.Offset(2, 0).Activate
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
MsgBox ("activate a cell 2 columns to right")
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 2).Activate
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
MsgBox ("activate a cell 3 rows above the active cell")
ActiveCell.Offset(-3, 0).Activate
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
MsgBox ("activate a cell 4 columns to left")
ActiveCell.Offset(0, -4).Activate
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
MsgBox ("activate a cell 3 rows below and 2 columns to right")
ActiveCell.Offset(3, 2).Activate
ActiveCell.Interior.Color = RGB(random, random, random)
End SubWe are taking the active cell as C3.
This was all about using Active Cell in VBA.
Thank you for reading. ❤
